Mathematical Logic
Logic has been used for thousands of years, from philosophy to mathematics and now to artificial intelligence. Logic is concerned with the truth and falsity of statements. The logic we will be studying will be answering the question: “when does a statement follow from a set of statements?”
Note to the reader
I have previously written about logic here and therefore this article will be relatively short when it comes to explaining everything about logic. If you want to understand logic, please read the article I have written on logic. This is just an expansion on what we have learned.
Propositional logic
Propositions can only be true or false.
Intrepetations
An intrepretation assigns to a propositional statement a truth value of True or False. True or False can be represented as 0 and 1 respectively.
Propositional symbols
There are about 500,000 ways to represent logic symbols so here are the most common ways
Not
Symbol in logic
¬ or ! or ~

What does it do
Inverts what is ever inputted into it.

Conjunction or and
Symbol in logic
^ or AND or ,

What it does
Takes >1 inputs and if both inputs are true, outputs true.

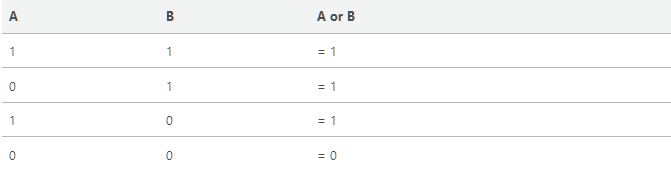
Disjunction, “or”
Symbol in Logic
V, or, “OR”

What it does
Takes > 1 inputs, if any of the inputs are true than the output is true.
Equivilance
Symbol in Logic <=> or ≡
Symbol in Electronics None, this is a concept not a gate.
What it does A and B must take the same truth value
Truth Table
A B A <=> B 1 1 = 1 0 1 = 0 1 0 = 0 0 0 = 1
Implication
Symbol in Logic => or “if a then b”
Symbol in Electronics None
What it does If A is true then so is B

https://www.dyclassroom.com/boolean-algebra/propositional-logic-truth-table Sorry for the change of pictures. Previously there was an error in this truth table.
Truth under an interpretation
Given an interpretation, I, we can compute the truth value of any formula P under I. That is, given a version of the formula we can computer the truth value.
if I(P) = 1 then we say that P is true under interpretation I. if I(P) = 0 then we say that P is false under interpretation I.
Logical Puzzles
This section may help the reader in understanding logical puzzles.
An island has two kinds of inhabitants, knights, who always tell the truth, and knaves, who always lie. You go to the island and meet A and B. A says that “B is a knight” B says that “The two of us are opposite types”
What are A and B?
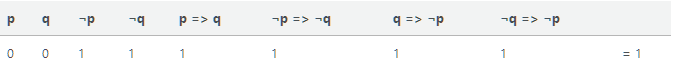
So we have 2 options, p: “A is a knight”; and q: “B is a knight”
We have 2 options because one of them needs to be a knight. Either both A and B are knaves, which makes B a knight as it told a truth so it lied or A is a knight and is telling the truth that B is a knight.
Options for person A p is true, that is the statement “A is a knight” is true. P => Q p is false, that is the statement “A is a knight” is false. ¬P => ¬Q
Options for person B q is true then q => ¬p q is false then ¬q => ¬p
Now we simply need to construct a truth table for these values
p q ¬p ¬q p => q ¬p => ¬q q => ¬p ¬q => ¬p 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 = 1
Then we stop here because we’ve found an interpretation under which they are both knaves which is satisfiable.
Semantic Conseqeuence
Note: The lecture slides for this weren’t helpful and there is no audio for this. Please message me what this is.
Digital Logic Circuits
Modern computers use logic gates to operate. You should have an understanding of logic gates from the above.
General house keeping rules of making circuits
Never combine two input wires
If there are 2 separate inputs, A and B, you cannot combine them into one single wire.
A single input wire can be split partway and used as input for two seperate gates
If you have a single input, A, it can be split into 2 separate wires.
An output wire can be used as input
The output of a wire can be used as an input.
No output of a gate can eventually feed back into that gate
No gates can loop on themselves.
Constructing logic circuits from tables
Given a table, such as the one below, how would we construct a logic circuit for it?

First, work out where it is equal to 1 (true) and then from there formalise it in mathematical logic, from the mathematical logic we can deduce the circuit for it. Sometimes it is easier to guess directly what logic gates are used.
Circuit equivalence
Two circuits are equivalent if they produce the same output given the same input
Formula equivalence
2 formula are equivalent if they hold the same truth value under every possible interpretation.
On Logical Equivalence
The symbol “≡” is used to show an equivalence relation.
Facts
≡ is reflexive ≡ is transitive ≡ is symmetric
Simplfying propositonal formulae
There are some rules we can use to simplfy propositional formulae.
Communicative Law
AB = BA, A + B = B + A
Examples: 6 * 2 = 12 and 2 * 6 = 12 3 + 4 = 7 and 4 + 3 = 7
Assiocative Law
a(bc) = ab(c) = abc
Examples: (2 + 4) + 5 = 6 + 5 = 11 2 + (4 + 5) = 2 + 9 = 11
Distributive Law
a(b+c) = ab + ac
Example: 3 × (2 + 4) = 3 * 6 = 18 3 × 2 + 3 × 4 = 6 + 12 = 18
Demorgans’ Laws
(A ∪ B)’ = (A)’ ∩ (B)’ The first law states that the complement of the union of two sets is the intersection of the complements.
(A ∩ B)’ = (A)’ ∪ (B)’ The second law states that the complement of the intersection of two sets is the union of the complements.
For a good blog post on understanding these laws, click (here)[https://brilliant.org/wiki/de-morgans-laws/]
Miscelanous rules
Not Not A = A A or A and B = A A or not A and B = A and B (A or B) (A or C) = A or B and C
What to do next From this point, turn the circuit into a logical expression and simplfy it using the rules above.
If this is confusing still, maybe this video will help: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=59BbncMjL8I
Boolean Functions
Arity The arity of a boolean function is how many arguments the function takes
Boolean function representation
Any boolean can be represented with ^, v, or ¬.
Logic Gates Extended
In this section we will explore logic gates some more, by looking at the family of not / exclusive gates.
XOR
Symbol in Logic
None

What it does
An XOR gate takes >1 inputs and performs exclusive disjunction. The output of an XOR gate is only true if one of its inputs is different to the other input.

NAND
Symbol in Logic
None

What it does
A NAND gate takes >1 inputs and the output is the opposite of an AND gate. The output is true when one or more, but not all, of its inputs are false.

Universality of XOR and NAND
All boolean functions can be created using either XOR or NAND gates.
Binary Numbering System
Binary is a numbering system that consists of 0 and 1s.

Alternatively, you could memorise the powers of 2. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024… And then to convert a number into binary, let’s say 6, you build that up from the different powers. So 6 is 011 and then reverse that, 110
Binary Addition
Somethings you need to know in binary 0 + 0 = 0 1 + 0 = 1 0 + 1 = 1 1 + 1 = 10
Once you know these basic rules, you can add any numbers together in binary the same way you can add normal numbers. Try this exercise
011
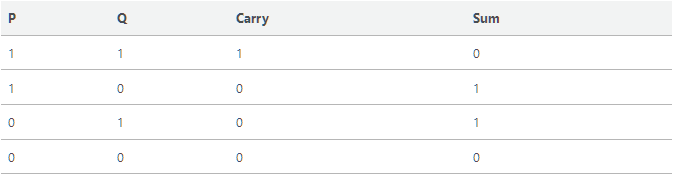
half-adder
The half adder is a type of binary adder in electronics that adds together two single binary digits and provides the output plus a carry value.

Note: Boris’ half-adder is overcomplicated, you can achieve the same by replacing 3 of his logic gates with a single XOR gate.
Truth Table
Full-adder
The full adder allows you to carry-in as well as carry-out.

Watch this video for a better understanding
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VPw9vPN-3ac
Black Box Notation
We can represent the full adder as a black box, we don’t need to know what happens inside of it, only the inputs and outputs.

4 bit adder
Using blackbox notation, we can create 4-bit adder
http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/combination/comb_7.html
Computer Representation of negative integers
A fixed number of bits is used to represent integers: 8, 16, 32 or 64 bits. An unsigned integer can take up all the space available.
You can “sign” a binary number to indicate whether it is negative or not. For example, the number 10 can be represented in 8-bit as 00001010 and -10 can be represented in 8-bit as 10001010
But this sometimes causes a problem, for example, 10000000 represents -0. Whaaatt?? Negative 0? Yes! That’s right, and that’s exactly the problem this causes.
This is where 2’s complement comes into play.
Twos complement
Converting a decimal to twos complement
- Convert the number to binary, ignoring the sign for now. So 5 is 0101 and -5 is 0101.
- If the number is a positive number then you are done, no need to go any further. Otherwise…
- If the number is negative then:
- Find the complement (EG convert all 0’s to 1’s and all 1’s to 0’s)
- Add 1 to the complement
- 1101 1100 with a carry of 1 that goes all the way to the left, it can be ignored.
